Is it possible to become a leader hospital in organ donation in a short period of time?
Ernesto Duarte Tagles1,3, Martha Susana Pérez Cornejo2,4, Natalia Rodríguez Payán2,4, Luis Carlos Rodríguez Sancho1,3, Alejandro René Bernal Yanes2, María Fernanda Félix Rodríguez5, Daniel Rosas Salazar5.
1Department of transplantation, Hospital General del Estado "Dr. Ernesto Ramos Bours", Hermosillo, , Mexico; 2Organ Donation Coordination, Hospital General del Estado "Dr. Ernesto Ramos Bours", Hermosillo, , Mexico; 3Department of transplantation, Hospital CIMA Hermosillo, Hermosillo, , Mexico; 4Organ Donation Coordination, Hospital CIMA Hermosillo, Hermosillo, , Mexico; 5Escuela de Medicina, Universidad de Sonora, Hermosillo, , Mexico
Introduction: when criteria for Brain Death were established and Organ Donation from such potentials donors (DBD) was recognized, hope of a cure for patients in need of a transplant increased. Soon after, difficulties of the process were notorious. In México, General Health Law states how organ donations should run and establishes that every hospital must have a specific license to do organ procurement (reason why most hospitals in México can´t proceed with an organ donation). Hospitals must have an Organ Donation Coordinator, who has special training given by CENATRA. This person must do all work directed to get as many donations are possible: intrahospital education, protocols to detect, follow and determine suitabilty of potential donors; is the only person authorized to talk to families to get consent donation as well. In this study, we want to show how a hospital, with people working specifically in organ donation with a program aim to get more donors through close work interaction with transplant department to create confidence, awareness and importance to become a donor, can increase donation and become a nationwide leader.
Method: we collected data for every death considered potential organ donors since 1982, when kidney transplant program started and separated in two groups: from 1982-2007 and 2008-2023, before and after a transplant department and organ donation coordination were created. We obtain data on number of BD and of consented and not consented donations.
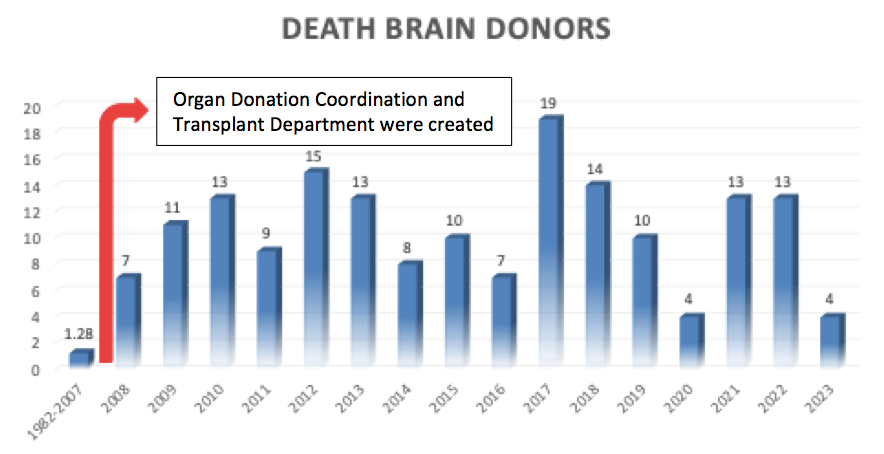
Result: from 1982 to 2007 the average of DBD in our hospital was 1.82 donors per year.In 2008, when the organ donation coordination was created, number of donors raised up to 7 and constantly did for the next years.
The percentage of consent is 78% and only 10% of not consent to donate is because express negative.
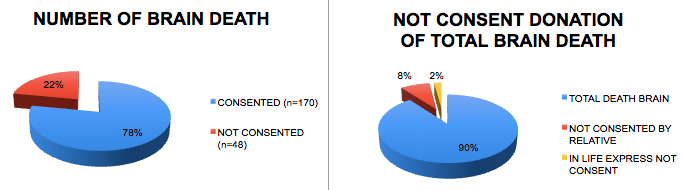
In 2012, our hospital appeared by the first time ranked in the top 5 hospitals with most DBD nationwide and over the last 10 years, has appeared 7 times in this list, being 2nd place three time in 5 years. In 2021, death donor rate was 17.2 pmp. Total of DBD since 2008 is 170, median age 39 years, 68% male and 32% female.
Conclusions: we think it is possible to increase number of donations relatively fast and keep high frequency. Our proposals to have these results are, regarding the Organ Donation Coordinator:
Finally, legislation regarding special license to be a donor hospital should be revised, since a lot of potential donors can be loose only because hospital is not allowed.